How Wankel Rotary Engines Work
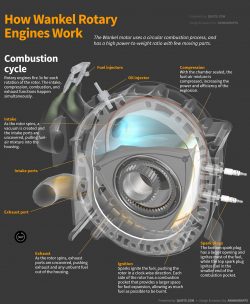
Combustion cycle
Rotary engines fire 3x for each rotation of the rotor. The intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust functions happen simultaneously.
Fuel injectors
Oil injector
Compression
With the chamber sealed, the fuel-air mixture is compressed, increasing the power and efficiency of the explosion.
Intake
As the rotor spins, a vacuum is created and the intake ports are uncovered, pulling fuel-air mixture into the housing.
Intake ports
Exhaust port
Exhaust
As the rotor spins, exhaust ports are uncovered, pushing exhaust and any unburnt fuel out of the housing.
Ignition
Sparks ignite the fuel, pushing the rotor in a clock-wise direction. Each side of the rotor has a combustion pocket that provides a larger space for fuel expansion, allowing as much fuel as possible to be burnt.
Spark plugs
The bottom spark plug has a larger opening and ignites most of the fuel, while the top spark plug ignites fuel in the smaller end of the combustion pocket.
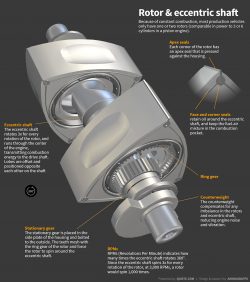
Rotor & eccentric shaft
Because of constant combustion, most production vehicles only have one or two rotors (comparable in power to 3 or 6 cylinders in a piston engine).
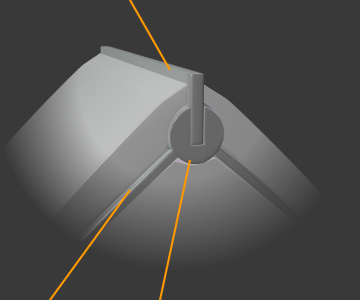
Apex seals
Each corner of the rotor has an apex seal that is pressed against the housing.
Face and corner seals
retain oil around the eccentric shaft, and keep the fuel-air mixture in the combustion pocket.
Eccentric shaft
The eccentric shaft rotates 3x for every rotation of the rotor, and runs through the center of the engine, transmitting combustion energy to the drive shaft. Lobes are offset and positioned opposite each other on the shaft
Ring gear
Counterweight
The counterweight compensates for any imbalance in the rotors and eccentric shaft, reducing engine noise and vibration.
Stationary gear
The stationary gear is placed in the side plate of the housing and bolted to the outside. The teeth mesh with the ring gear of the rotor and force the rotor to spin around the eccentric shaft.
RPMs
RPMs (Revolutions Per Minute) indicates how many times the eccentric shaft rotates 360°. Since the eccentric shaft spins 3x for every rotation of the rotor, at 3,000 RPMs, a rotor would spin 1,000 times.
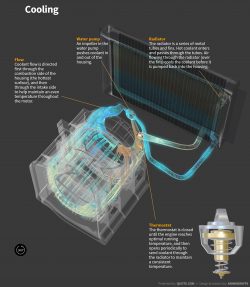
Cooling
Flow
Coolant flow is directed first through the combustion side of the housing (the hottest surface), and then through the intake side to help maintain an even temperature throughout the motor.
Water pump
An impeller in the water pump pushes coolant in and out of the housing.
Radiator
The radiator is a series of metal tubes and fins. Hot coolant enters and passes through the tubes. Air flowing through the radiator (over the fins) cools the coolant before it is pumped back into the housing.
Thermostat
The thermostat is closed until the engine reaches optimal running temperature, and then opens periodically to send coolant through the radiator to maintain a consistent temperature.
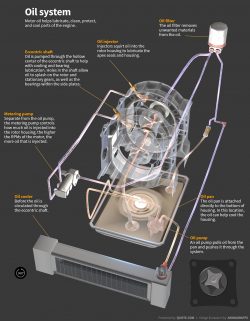
Oil system
Motor oil helps lubricate, clean, protect, and cool parts of the engine.
Eccentric shaft
Oil is pumped through the hollow center of the eccentric shaft to help with cooling and bearing lubrication. Holes in the shaft allow oil to splash on the rotor and stationary gears, as well as the bearings within the side plates.
Oil injector
Injectors squirt oil into the rotor housing to lubricate the apex seals and housing.
Oil filter
The oil filter removes unwanted materials from the oil.
Metering pump
Separate from the oil pump, the metering pump controls how much oil is injected into the rotor housing; the higher the RPMs of the motor, the more oil that is injected.
Oil cooler
Before the oil is circulated through the eccentric shaft.
Oil pan
The oil pan is attached directly to the bottom of housing. In this location, the oil can help cool the housing.
Oil pump
An oil pump pulls oil from the pan and pushes it through the system.
The full model
References
- How Rotary Engines Work - Mazda RX-7 Wankel - Detailed Explanation. (2016). YouTube. Retrieved 14 December 2016, from https://youtu.be/sd6pJtR4PaY
- How To Build A Rotary Engine. (2016). YouTube. Retrieved 14 December 2016, from https://youtu.be/LSEs8VXzVPU
- Rotary Engine Buildup (NEW!) Custom 3 Rotor Turbo Bridgeport Race Engine. (2016). YouTube. Retrieved 14 December 2016, from https://youtu.be/AQ4SLg5tXVE
- Rotary Engine Lubrication System. (2016). YouTube. Retrieved 14 December 2016, from https://youtu.be/ESVouiAVyXg
- Aircraft Rotary Engine News Letter. (2017). Rotaryeng.net. Retrieved 31 March 2017, from http://www.rotaryeng.net/
- How a rotary Wankel engine works. (2016). How a Car Works. Retrieved 14 December 2016, from https://www.howacarworks.com/technology/how-a-rotary-wankel-engine-works
- Thermal view of Liquid Piston's new diesel rotary engine compared to a traditional Wankel rotary engine.. (2016). Imgur. Retrieved 14 December 2016, from http://i.imgur.com/jGsHqoS.gifv
- RX-8 Help. (2017). Rx8help.com. Retrieved 31 March 2017, from http://www.rx8help.com/home/overview.html
Share / embed code
• Copy/paste the code below to share this project on your site (in an iframe).
• We only require a link back to this page and name attribution (ex: "by Quote.com")
Sharing images
(click for large versions)